In a recent article I wrote that California's biggest danger to water reliability isn't the lack of dams or groundwater, it was the State's growth policy that's forces city's to build. In its drive to produce housing to meet a desktop analysis that says the state will grow to ~51 million people, the state uses a little known legislative law called RHNA that 'tells cities' throughout the state how many units they must provide for. The cities must then answer in response by identifying properties (and even re-zone to allow for higher densities) where developers can build those units if the properties become available on the market.
Recently a news article listed Nine California cities running out of water. Most of them are in the central valley where it is especially bad. To emphasis how disconnected the State's RHNA process to the water challenges that cities face, I've provided is a list of those nine cities along with the number of units each city's is allocated to provide for and a rough estimate1 on how much water will be needed to support those units should they be built out.
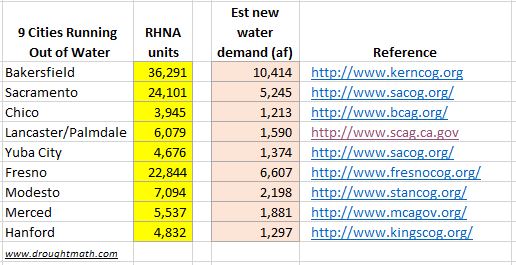
On one hand each of theses cities are confronted with a huge water deficit resulting in an unreliable water supply and on the other hand the State is pushing them to increase housing in places where its no longer practical. Literally RHNA is running cities out of water. The housing allocations are running up water demand to the point where cities have insufficient supplies.
Between the 2006/2013 and 2014/2021 RHNA allocations, the City of Los Angeles has had to identify properties that could be developed for 194,000 units.
Updated 7/31/15
In the most recent Water Board Water Conservation Report, LADWP has been revising population figures presumably to keep the Residential-GPCD level from getting out of control. They are now projecting monthly population growth and using each months figures to calculate residential water use. The screen shot from the report shows the city has projected that it has grown by 55,089 residents while the water supply has dropped.
RHNA forces cities to identify properties that are suitable for development for the number of units they are allocated for. Despite the 7 year long water deficit the city has been fighting, the increasing population numbers that the LADWP is providing is a result of the California's RHNA requirement. If a developer want to build on a property identified in the Housing Element (a RHNA requirement), the city can't say no.
1RGPCD data in the May '15 Urban Water Supplier Report was used as a basis for each cities demand.
